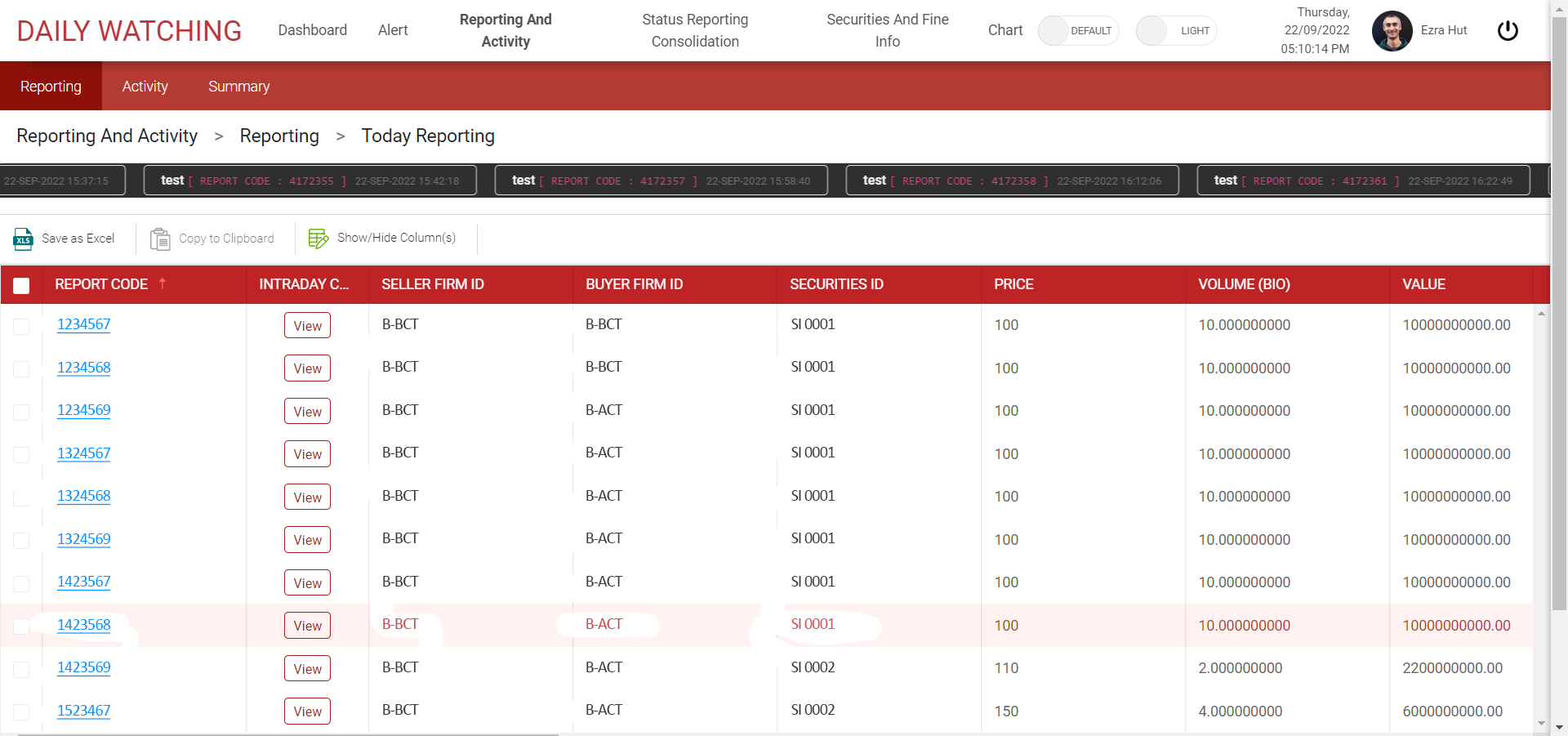
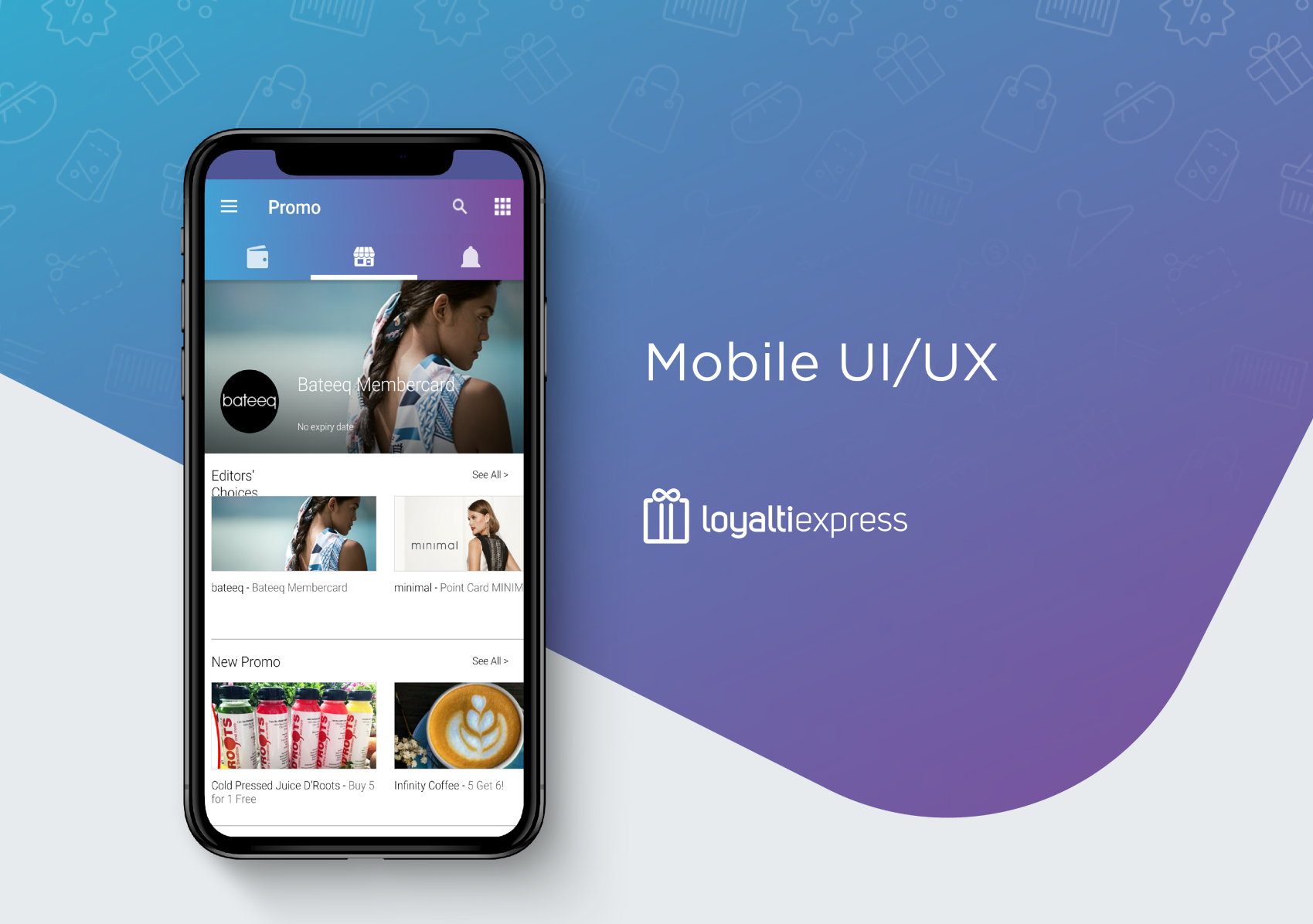
There are three main options for creating a mobile app: Native, Web & Hybrid Apps. You can create a native app, a hybrid app or a web app. Here we’ll look at the advantages and disadvantages of each option and how to choose the best development path for your projects.
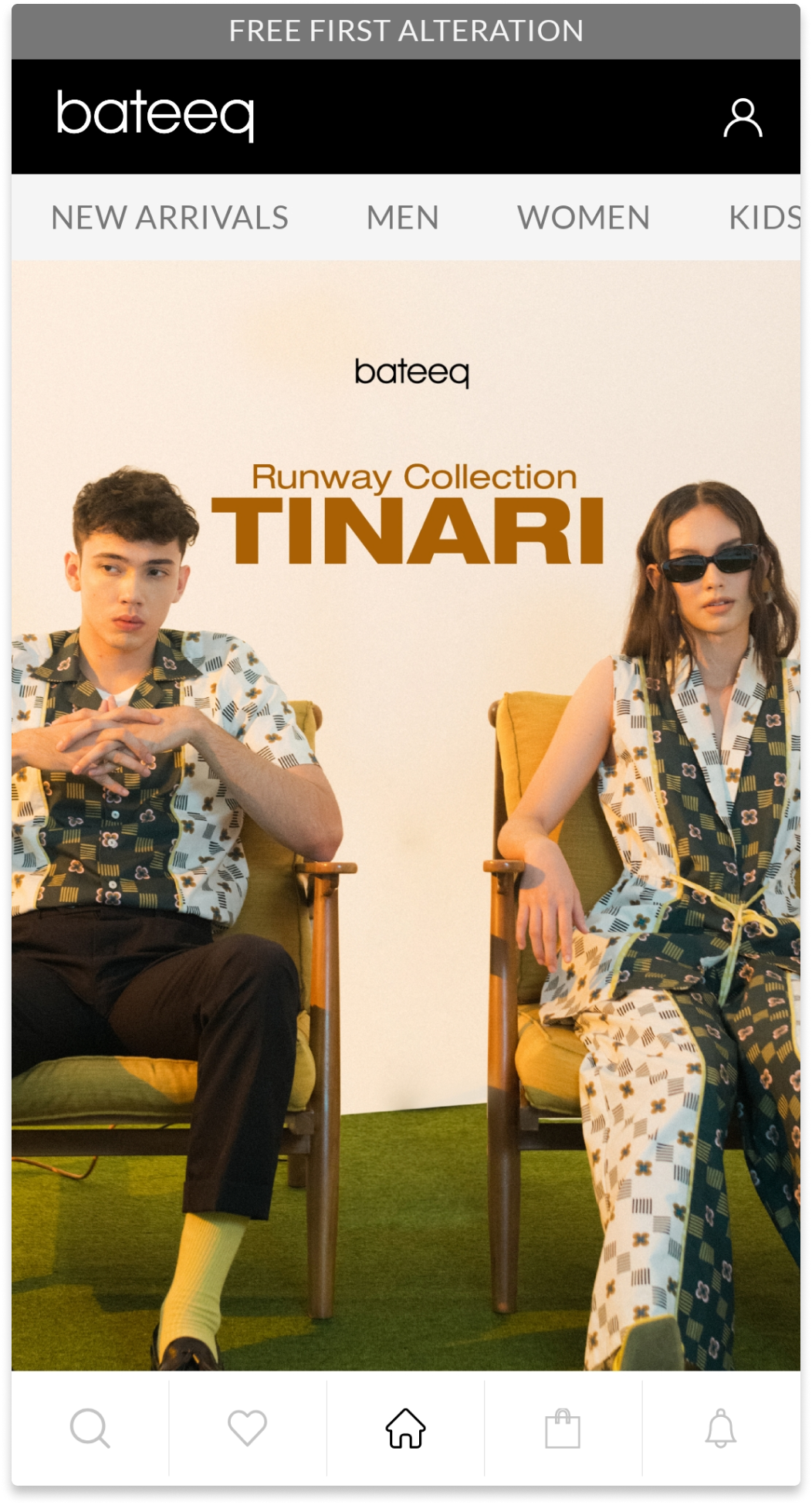
Native Apps
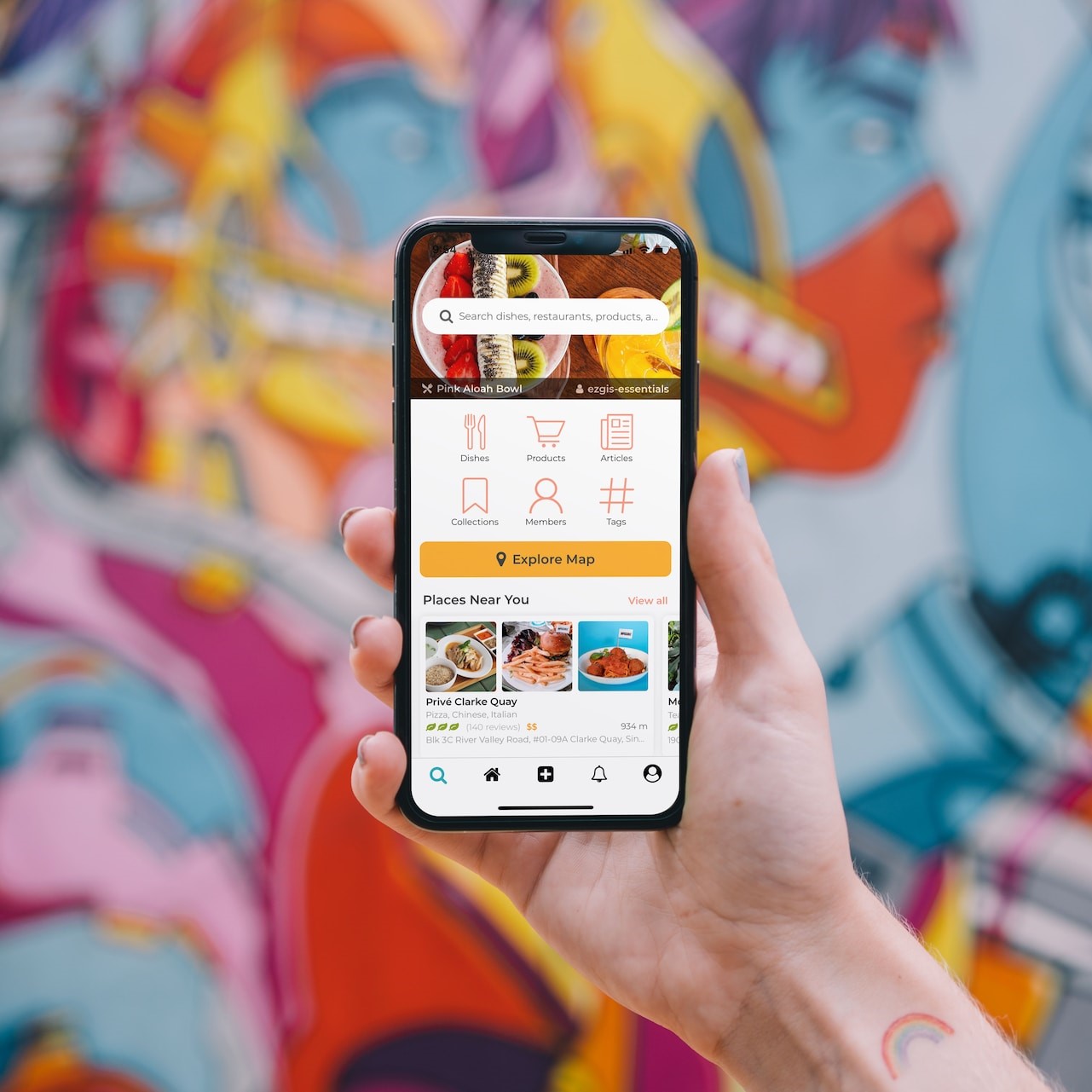
Native apps live on the device and are accessed through icons on the device home screen. Native apps are installed through an application store (such as Google Play or Apple’s App Store). They are developed specifically for one platform, and can take full advantage of all the device features — they can use the camera, the GPS, the accelerometer, the compass, the list of contacts, and so on. They can also incorporate gestures (either standard operating-system gestures or new, app-defined gestures). And native apps can use the device’s notification system and can work offline.
For example of native apps are Pokemon GO, Adobe Lightroom, Spotify, and many more.
Web Apps
Web apps are not real applications; they are really websites that, in many ways, look and feel like native applications, but are not implemented as such. They are run by a browser and typically written in HTML5. Users first access them as they would access any web page: they navigate to a special URL and then have the option of “installing” them on their home screen by creating a bookmark to that page.
Web apps became really popular when HTML5 came around and people realized that they can obtain native-like functionality in the browser. Today, as more and more sites use HTML5, the distinction between web apps and regular web pages has become blurry.
For example of native apps are Google Mail, Youtube, Google Maps, and many more.
Hybrid Apps
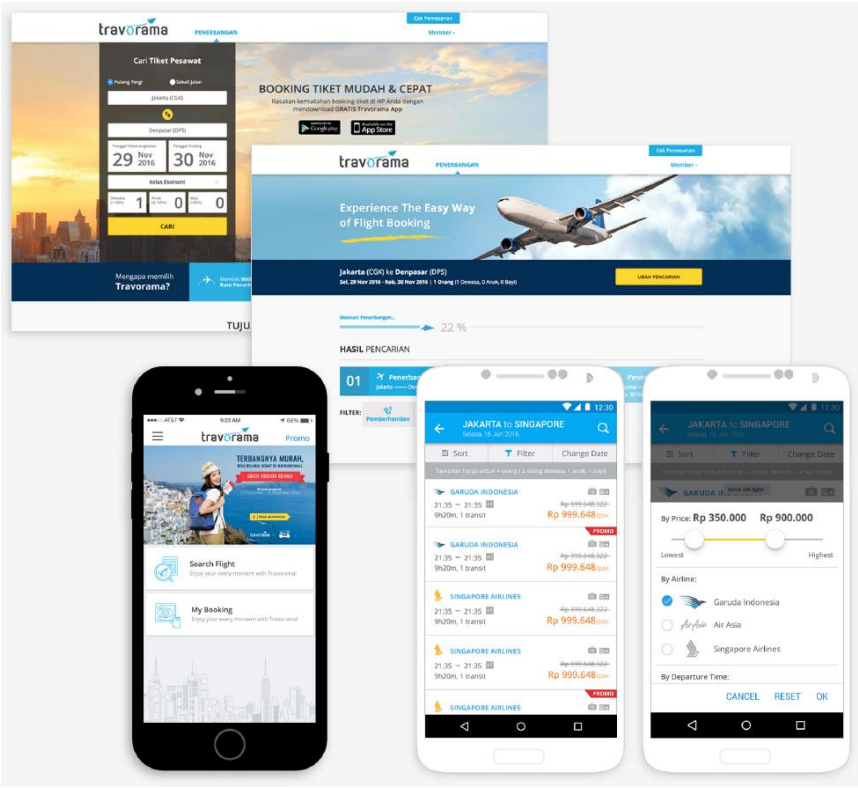
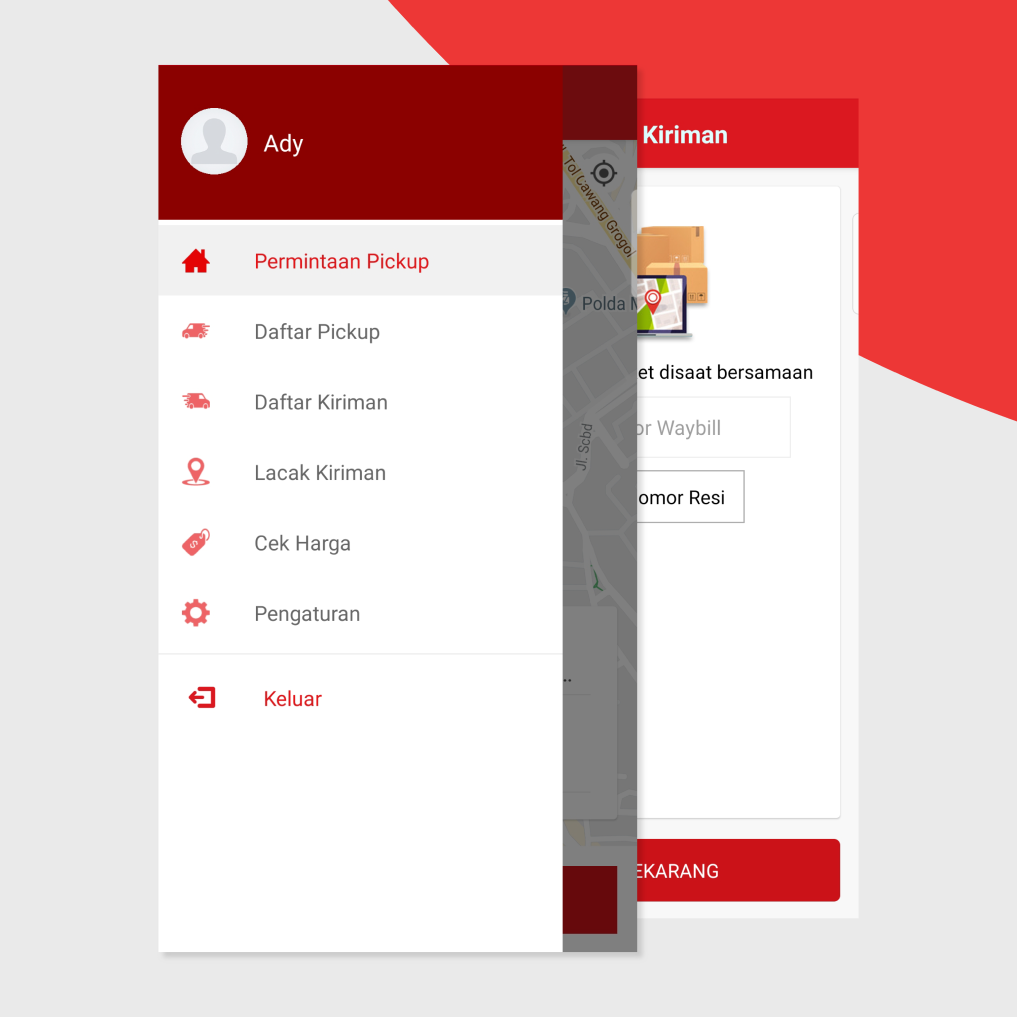
Hybrid apps are part of native and web apps. Like native apps, because they live in an app store and can take advantage of the many device features available. Like web apps, they rely on HTML being rendered in a browser, with the caveat that the browser is embedded within the app.
The biggest advantage of hybrid apps is that they enable support for multiple operating systems at a more cost-effective price point than multiple native apps. For a well-developed app, users will not normally be able to distinguish whether an app is native or hybrid. Users generally don’t care about your app’s development process, they just care if it works on their device and does what they expect it to do.
There are disadvantage to hybrid app development. It can present serious challenges if the app requires complex interaction from the device, there’s a limit to what plugins can achieve on this front. The costs of upkeep on a hybrid application may be higher than the costs of a native app.
For example of native apps are Instagram, AirBnb and many more.
So, Which Should You Choose: Native, Web or Hybrid Apps
If you need an app that is highly customized and performs well, then a native app is the best choice. If you are on a budget, then try hybrid app. But, if you just need a simple app that doesn’t need to access any device feature, then a web-based mobile app is the way to go.
Get in touch with us today to learn more or find us on Instagram to get insight!